SAP HANA - In memory Key concepts
Minimizing data movement
Sap Hana Architecture
Sap Hana Database
SAP HANA - Data persistence
SAP HANA - HINTS
The second key to improving data processing performance is
to minimize the movement of
data within the database and between the database and the
application.
This section describes measures to achieve this target.
Compression
Even though today’s memory capacities allow keeping enormous
amounts of data in-memory, compressing the data in-memory is still
desirable. The goal is to compress data in a way that does not use up performance gained, while still
minimizing data movement from RAM to the processor.
By working with dictionaries to be able to represent text as
integer numbers, the database can
compress data significantly and thus reduce data movement,
while not imposing additional CPU load for decompression, but even adding to the
performance.
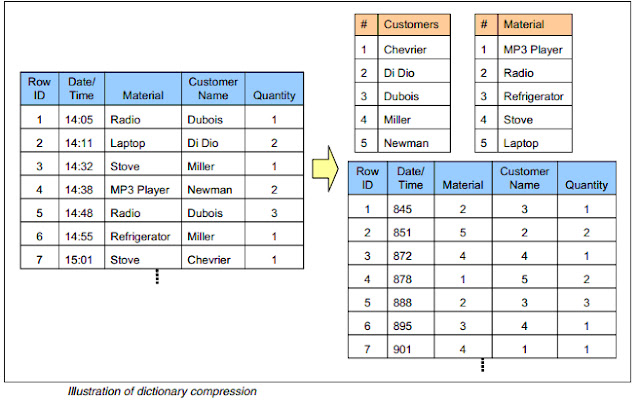
On the left-hand side of this figure the original table is
shown containing text attributes (that is, material and customer name) in their original
representation. The text attribute values are stored in a dictionary (upper right), assigning an integer
value to each distinct attribute value.
In the table the text is replaced by the corresponding
integer value as defined in the dictionary. The date/time attribute has also been converted
to an integer representation.
Using dictionaries for text attributes reduces the size of
the table, because each distinct attribute value has only to be stored once, in the
dictionary, so each additional occurrence in the table just needs to be referred to with the
corresponding integer value.
The compression factor achieved by this method is highly
dependent on data being compressed. Attributes with few distinct values compress
very well, whereas attributes with many distinct values do not benefit as much.
While there are other, more effective compression methods
that could be employed with in-memory computing, to be useful, they must have the
correct balance between compression effectiveness, which gives you more data in your
memory, or less data movement (that is, higher performance), resources needed for
decompression, and data accessibility (that is, how much unrelated data has to be
decompressed to get to the data that you need). As discussed here, dictionary compression
combines good compression effectiveness with low decompression resources and high data
access flexibility.
Sap Hana Architecture
Sap Hana Database
SAP HANA - HINTS

Comments
Post a Comment